Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions that cause fear, dread and other symptoms that are out of proportion to the situation. There are several types, including generalized anxiety disorder, specific phobias and social anxiety disorder.
Anxiety is a natural reaction which the human body secretes adrenal as a result of stress stimuli. Increased heart rate and more blood flow to the brain result from this hormone release. Extra oxygen enables us to think clearly and focus on problems at hand.
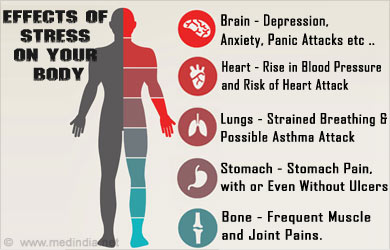
However, if we are always afraid or under pressure, it is dangerous. Preoccupations like being late for appointments; missing deadlines; losing objects; feeling shy in company can keep a person under permanent stress conditions. This continuous state leads to emotional disorders such as permanent fear or worry and somatic illnesses including headaches, muscle pain etc.
Chest Pain and Discomfort
Anxiety can manifest physically in your chest, often leading to alarming sensations that mimic heart problems. You may experience tightness, pressure, or a sharp, stabbing pain in your chest during anxiety attacks. These symptoms can be frightening, causing you to worry about potential cardiac issues.
Understanding the Mechanism
When anxiety strikes, your body’s stress response kicks into high gear. This “fight or flight” mode triggers the release of stress hormones like adrenaline, which can cause your heart to race and your chest muscles to tense up. The resulting discomfort can range from mild to severe, often lasting for several minutes or even hours.
Distinguishing from Heart Problems
It’s crucial to recognize that while chest pain from anxiety can be distressing, it’s generally not dangerous. However, since the symptoms can be similar to those of a heart attack, it’s always wise to seek medical attention if you’re unsure about the cause of your chest pain. Your doctor can help differentiate between anxiety-related chest discomfort and more serious cardiac conditions.
Remember, managing your anxiety through stress-reduction techniques and professional help can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of these chest symptoms, improving your overall quality of life.
Headaches and Migraines
Anxiety can be a real pain in the head—literally. When you’re grappling with anxious thoughts, your body’s stress response kicks into high gear, potentially triggering tension headaches or even debilitating migraines.
The Tension-Anxiety Connection
Anxiety often leads to muscle tension, particularly in the neck and shoulders. This tension can radiate upwards, causing a tight band-like sensation around your head. Over time, this persistent muscle contraction may result in frequent tension headaches, characterized by a dull, aching pain.
Migraine Mayhem
For some, anxiety doesn’t stop at tension headaches. It can be a potent trigger for migraines, those intense, throbbing headaches often accompanied by nausea and sensitivity to light and sound. The stress hormones released during anxious episodes can cause blood vessels in the brain to constrict and then dilate, potentially setting off a migraine attack.
Breaking the Cycle
While the link between anxiety and head pain is clear, there’s hope. Managing your anxiety through relaxation techniques, therapy, or medication can help reduce the frequency and intensity of these headaches. Remember, your mental health and physical well-being are closely intertwined. By addressing your anxiety, you’re not just easing your mind—you’re potentially saving yourself from a world of hurt.
Digestive Issues
Anxiety can wreak havoc on your digestive system, leading to a range of uncomfortable symptoms. When you’re anxious, your body enters a state of heightened alertness, triggering the “fight or flight” response. This physiological reaction can significantly impact your gastrointestinal tract.
Stomach Discomfort
You may experience a churning sensation in your stomach, often described as “butterflies.” This feeling can escalate to nausea or even vomiting in severe cases. Anxiety can also cause your stomach to produce excess acid, potentially leading to heartburn or indigestion.
Long-Term Consequences
Chronic anxiety can contribute to more serious digestive issues over time. You may be at higher risk for developing conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Additionally, the constant state of stress can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to gastrointestinal infections.
To manage these symptoms, it’s crucial to address your anxiety through stress-reduction techniques, therapy, or medication as recommended by a healthcare professional. Maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise routine can also help alleviate digestive discomfort associated with anxiety.
Muscle Pain and Weakness
Anxiety doesn’t just affect your mind; it can take a significant toll on your body as well. One of the most common physical manifestations of anxiety is muscle pain and weakness. This can leave you feeling drained and uncomfortable, impacting your daily life in unexpected ways.
Tension and Soreness
When you’re anxious, your muscles tend to tense up as part of the body’s natural “fight or flight” response. This prolonged tension can lead to soreness, especially in areas like your neck, shoulders, and back. You might find yourself unconsciously clenching your jaw or hunching your shoulders, exacerbating the discomfort.
Fatigue and Weakness
Constant muscle tension requires energy, leaving you feeling fatigued and weak. This exhaustion can make simple tasks feel challenging, affecting your productivity and overall quality of life. You may notice a decrease in your physical strength or endurance, even if you haven’t changed your exercise routine.
Long-term Effects
Chronic anxiety-induced muscle tension can lead to more serious issues over time. You might develop conditions like tension headaches, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, or even chronic pain syndromes. It’s crucial to address these symptoms early to prevent long-lasting effects on your musculoskeletal health.
Sleep Disturbances
Anxiety can wreak havoc on your sleep patterns, leading to a vicious cycle of restlessness and worry. When you’re anxious, your mind races with thoughts and concerns, making it difficult to relax and drift off to sleep. This can result in insomnia, characterized by trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early.
The Anxiety-Insomnia Connection
Your body’s stress response, triggered by anxiety, releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones are designed to keep you alert and ready for action, which is counterproductive when you’re trying to sleep. As a result, you may find yourself tossing and turning, unable to quiet your mind.
Impact on Sleep Quality
Even if you manage to fall asleep, anxiety can affect the quality of your rest. You might experience:
- Frequent nightmares or disturbing dreams
- Restless sleep with multiple awakenings
- Difficulty achieving deep, restorative sleep stages
Long-Term Consequences
Chronic sleep disturbances due to anxiety can lead to daytime fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. This, in turn, can exacerbate your anxiety, creating a self-perpetuating cycle that’s hard to break. Over time, persistent sleep issues can contribute to other health problems, including weakened immunity and increased risk of cardiovascular issues.
Understanding Anxiety Medications
Anxiety can be a debilitating condition, but there are effective medications available to help manage symptoms. Three commonly prescribed medications for anxiety are Valium, Ambien, and Xanax. These drugs belong to different classes and work in unique ways to alleviate anxiety and its related symptoms.
How These Medications Work
Valium (diazepam) is a benzodiazepine that enhances the effects of GABA, a neurotransmitter that reduces brain activity. This helps to calm nerves and relax muscles, providing relief from anxiety symptoms.
Xanax (alprazolam) is also a benzodiazepine, but it acts more quickly and is often used for panic attacks and severe anxiety episodes.
Ambien (zolpidem), while primarily a sleep aid, can indirectly help with anxiety by improving sleep quality. Many anxiety sufferers experience insomnia, and better sleep can lead to reduced anxiety symptoms during the day.
Considerations and Precautions
While these medications can be effective, it’s crucial to use them under a doctor’s supervision. They can be habit-forming and may have side effects. Your healthcare provider will consider your specific symptoms, medical history, and potential drug interactions before prescribing any anxiety medication.
Conclusion
As you’ve learned, anxiety can take a significant toll on your physical health in addition to your mental wellbeing. From digestive issues to cardiovascular problems, the effects of chronic anxiety on the body are wide-ranging and potentially serious. By understanding these physical manifestations, you’re better equipped to recognize anxiety’s impact and seek appropriate treatment.
Remember, anxiety is highly treatable through therapy, medication, lifestyle changes, or a combination of approaches. If you’re experiencing persistent anxiety and any of the physical symptoms discussed, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Taking action to manage your anxiety can dramatically improve both your mental and physical health.
